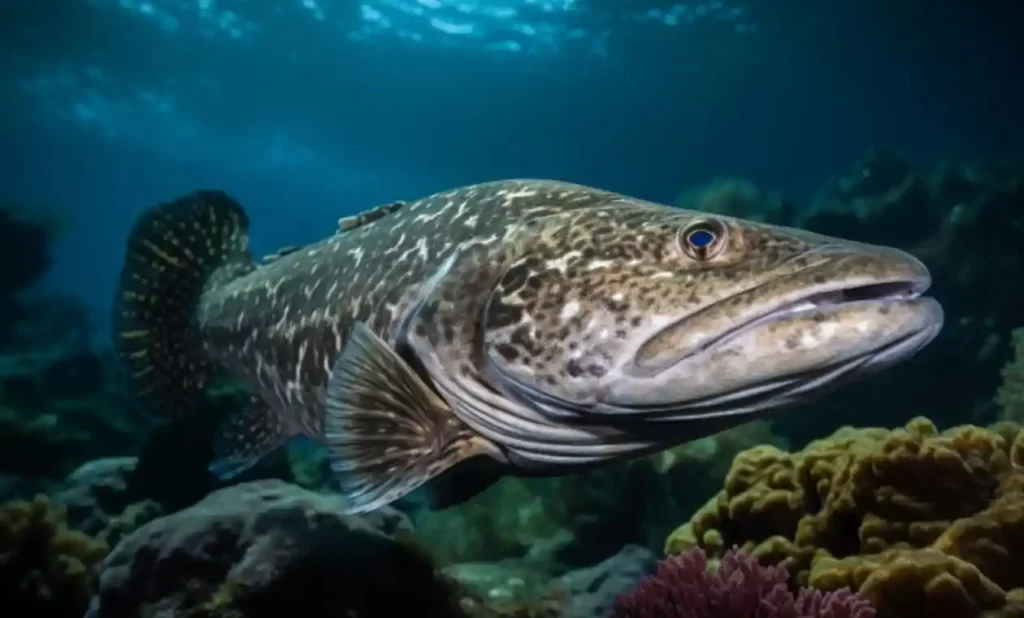
All About Cod Fish: Species, Fishing Techniques, Farming, and Benefits
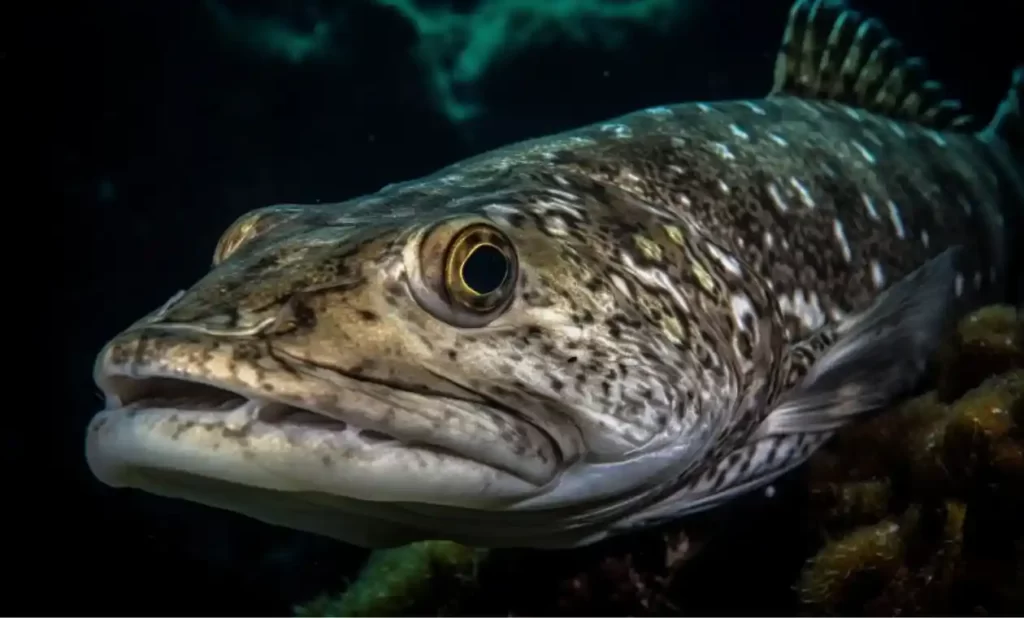

Welcome to the fascinating world of Cod Fish! In this article, we will explore the wonders of this remarkable species. Cod Fish, scientifically known as Gadus morhua, is a popular and widely recognized fish found in various parts of the world. From its unique appearance to its diverse habitats and intriguing lifestyle, Cod Fish has captured the curiosity of both scientists and seafood enthusiasts. Join us as we dive into the depths of knowledge about Cod Fish, uncovering interesting facts, health benefits, fishing techniques, conservation efforts, and much more. Let’s embark on an exciting journey to discover the secrets of this extraordinary creature!
Scientific Name
The scientific name of Cod Fish is Gadus morhua. The genus name “Gadus” comes from the Latin word for “cod” or “stockfish.” It is believed to be derived from the Celtic word “gad,” which means a “pole” or “stick,” referring to the traditional method of drying cod on wooden racks.
The species name “morhua” is derived from the Old Norse word “morrhūa,” which means “moorfish” or “dark fish.” This name is a reference to the fish’s dark coloration, especially on its back, which helps it blend with its surroundings in the deep waters where it often resides.
Together, the scientific name Gadus morhua reflects the historical and cultural significance of this species, as well as its distinct physical characteristics.
Length
The Cod Fish is known for its impressive length, often reaching considerable sizes. On average, Cod Fish can grow to be around 3 to 4 feet long, although some individuals can reach even greater lengths. The maximum recorded length of a Cod Fish is approximately 6 feet. It’s important to note that the length can vary depending on factors such as the age and habitat of the fish. These large dimensions contribute to the Cod Fish’s significance in both commercial fishing and recreational angling.
Weight
The weight of Cod Fish can vary significantly based on various factors, including age, habitat, and food availability. On average, adult Cod Fish typically weigh between 11 to 33 pounds. However, larger specimens have been recorded, with some reaching weights of up to 77 pounds or more. The weight of Cod Fish is highly valued in commercial fishing, as it is often used as an indicator of the fish’s size and potential yield. Whether you’re considering the smaller or the more massive Cod Fish, their weight plays a crucial role in their ecological and economic significance.
Top Speed
The Cod Fish is not known for its incredible speed compared to some other fish species. It generally swims at a moderate pace. On average, Cod Fish can achieve a top speed of around 15 to 20 miles per hour. However, it’s important to note that the swimming speed of Cod Fish can vary depending on factors such as age, health, and environmental conditions. While it may not be the fastest swimmer in the ocean, the Cod Fish’s ability to navigate its habitats with relative agility allows it to thrive in its natural environment.
Appearance and unique physique of Cod Fish
The Cod Fish possesses a distinct appearance and unique physique that sets it apart from other fish species. It has a long, slender body with a cylindrical shape and a slightly flattened head. The body is covered in small, smooth scales, which can vary in color depending on the fish’s habitat and age. Cod Fish typically display a range of shades, including olive-green, brown, or gray on their back, transitioning to a lighter color on their sides and belly.
One of the most prominent features of the Cod Fish is its large mouth, which extends to the back of its eyes. It is equipped with sharp, pointed teeth that aid in capturing and consuming its prey. Additionally, Cod Fish have a barbel, a fleshy whisker-like projection, on their lower jaw. This barbel helps them in locating food and sensing their environment.
Another unique physical characteristic of the Cod Fish is its prominent chin or “beard,” which consists of a small, whisker-like projection on the underside of its lower jaw. This beard is more pronounced in mature males and is believed to play a role in courtship and mating.
Overall, the appearance of Cod Fish combines sleekness, camouflage, and specialized adaptations that enable them to thrive in various marine environments. Their distinctive physique not only contributes to their survival but also adds to their charm and allure.
Types of Cod Fish
There are several different types of Cod Fish found in various parts of the world. The term “Cod Fish” is commonly used to refer to several closely related species within the genus Gadus. Some of the most well-known types of Cod Fish include:
Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua):
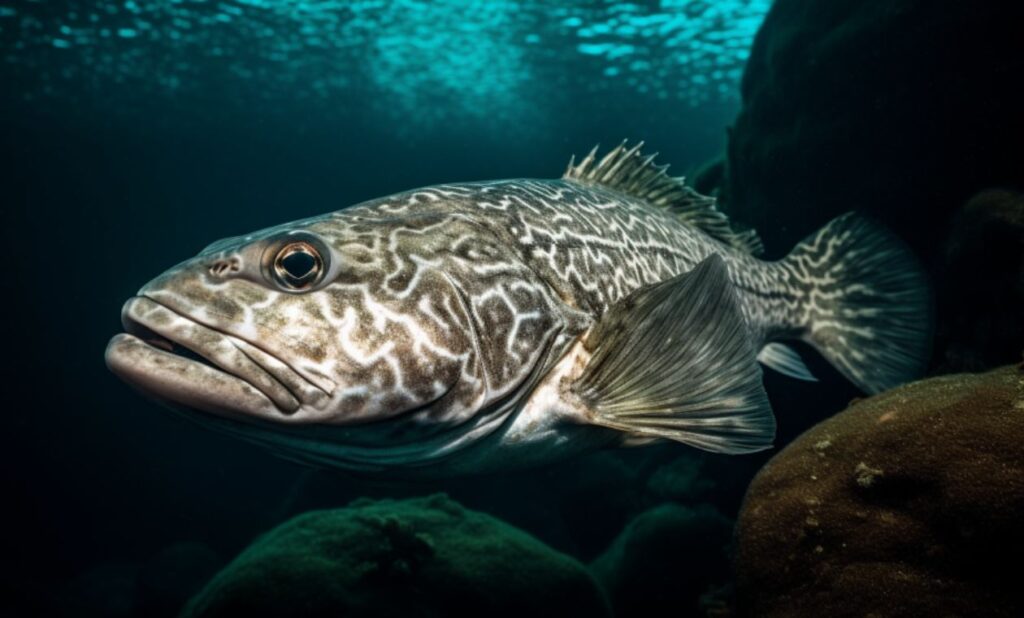

The Atlantic Cod holds a special status as one of the most iconic and economically significant fish species. It is primarily found in the cold waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, specifically in regions encompassing the coastal areas of North America and Europe.
In North America, the Atlantic Cod can be found along the eastern coast, ranging from Labrador and Newfoundland in Canada to the Gulf of Maine and as far south as Cape Hatteras in the United States. It is particularly associated with fishing grounds in the Gulf of Maine and the Georges Bank, where it has historically played a vital role in the fishing industry.
In Europe, the Atlantic Cod is abundant in the waters of the North Sea, the Norwegian Sea, the Barents Sea, and the waters around Iceland and Greenland. It is a species of great significance for countries such as Norway, Iceland, the United Kingdom, and Portugal, where it has supported thriving fishing communities for centuries.
The Atlantic Cod’s preference for cold waters and its ability to adapt to various depths make it well-suited to the North Atlantic’s unique ecosystem. Its availability in coastal regions has not only sustained traditional fishing practices but has also contributed to the development of local economies.
However, it is worth noting that the Atlantic Cod population has faced challenges due to overfishing and environmental factors. Conservation efforts and sustainable fishing practices have become crucial to ensuring the long-term viability of this iconic species.
The Atlantic Cod’s historical and cultural importance, coupled with its significance in commercial fisheries, make it a key focus of research, conservation initiatives, and management strategies aimed at preserving its populations and sustaining the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
Pacific Cod (Gadus macrocephalus):

The Pacific Cod is a species of fish that is primarily found in the northern Pacific Ocean. It inhabits the waters off the coast of Alaska, as well as regions near Russia, such as the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk.
In terms of appearance and habits, the Pacific Cod shares similarities with its counterpart, the Atlantic Cod. It has a similar elongated body shape, cylindrical in nature, with a slightly flattened head. The Pacific Cod also possesses a distinct coloration, ranging from olive-green to brown or gray on its back, transitioning to a lighter color on its sides and belly.
Like the Atlantic Cod, the Pacific Cod is a commercially important species and supports valuable fisheries in the regions where it is found. It has become an important resource for countries like the United States and Russia, contributing to local economies and providing sustenance for coastal communities.
Due to its prevalence in colder waters, the Pacific Cod has adapted to survive in harsher environments. It is known to be a bottom-dwelling species, often found near the seafloor. This behavior aligns with its feeding habits, as the Pacific Cod primarily preys on other fish, crustaceans, and small invertebrates.
While the Pacific Cod and the Atlantic Cod share many similarities, including their appearance, habits, and commercial significance, they are distinct species that inhabit different regions of the world. Each species has its own unique ecological role and plays a vital part in supporting local fisheries and marine ecosystems.
Greenland Cod (Gadus ogac):

The Greenland Cod, also referred to as the Arctic Cod, is a species of fish that primarily inhabits the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. It can be found in the waters surrounding Greenland, as well as in areas near Canada’s Arctic coast.
What sets the Greenland Cod apart is its remarkable adaptation to survive in extremely cold conditions. It thrives in frigid Arctic waters where temperatures can reach freezing levels. This species has evolved unique physiological and behavioral traits to endure such extreme environments.
Greenland Cod exhibit various adaptations that aid in their survival. Their bodies are well-suited to withstand low temperatures, featuring a thicker layer of fat and a dense musculature that helps them retain body heat. This adaptation enables them to thrive in icy waters that would be inhospitable to many other fish species.
Furthermore, the Greenland Cod is highly resilient to long periods of darkness and limited food availability, which are common in the Arctic region. Their metabolism adjusts to the scarcity of food during the winter months, allowing them to survive on meager resources until more abundant prey becomes available.
The Arctic Cod’s ability to adapt and thrive in these extreme conditions is of great ecological significance. It serves as a vital component of the Arctic food web, providing a source of sustenance for other predators, including marine mammals and seabirds.
Understanding and preserving the habitat of the Greenland Cod is crucial, especially as climate change continues to impact the Arctic ecosystem. The survival of this species is intricately linked to the delicate balance of Arctic marine life, making it an important focus of conservation efforts in the face of ongoing environmental challenges.
Rock Cod (various species):

“Rock Cod” is a term commonly used to describe various fish species that resemble true cod but do not belong to the same family. While they may share a similar appearance and sometimes inhabit rocky habitats, it’s important to note that these species are not true cod.
One example of a fish often referred to as “Rock Cod” is the Pacific Rockfish. These fish are found along the Pacific coast of North America, from Alaska to California. Pacific Rockfish come in a variety of colors and patterns, ranging from reddish-brown to olive-green. They are known for their spiny dorsal fins and robust bodies, which allow them to navigate rocky environments.
Another species sometimes called “Rock Cod” is the Atlantic Rock Cod. This fish, also known as the Tautog, is found along the eastern coast of North America, from Nova Scotia to Georgia. Atlantic Rock Cod have a stout, elongated body and are known for their dark coloration and powerful jaws. They are commonly found near rocky reefs and inshore areas.
While these species may be called “Rock Cod” due to their similar appearance, it’s important to differentiate them from true cod fish, such as the Atlantic Cod or Pacific Cod. Each of these species has its own unique characteristics, habitats, and ecological roles within their respective environments. Understanding these distinctions helps in accurately identifying and appreciating the diverse array of fish species in our oceans.
It’s important to note that while these are some of the most notable types of Cod Fish, there may be other regional or local variations and species that are referred to as “Cod Fish” in specific areas. Each type of Cod Fish has its own distinct characteristics, range, and importance in local fisheries.
Black Cod Fish

Black Cod, also known as Sablefish, is a species of fish that is not actually a member of the Cod family. Its scientific name is Anoplopoma fimbria. Despite the name, it is not closely related to true Cod fish.
Black Cod is primarily found in the North Pacific Ocean, ranging from the coast of Japan and Korea to Alaska and down to California. It prefers deep, cold waters and is often associated with rocky or muddy seabeds. Black Cod is known for its deep-water habitat, typically found at depths ranging from 1,000 to 4,000 feet.
One distinguishing feature of the Black Cod is its dark, almost black coloration, which gives it its common name. It has a slender, elongated body and a large head with a prominent jawline. The fish can grow to impressive sizes, with adults reaching lengths of up to 3 feet and weighing over 40 pounds.
Black Cod is highly regarded for its rich and buttery flavor, making it a popular choice among seafood enthusiasts. Its delicate, flaky flesh is prized in various culinary preparations, including grilling, broiling, and smoking. It is often featured in Asian cuisine, particularly in Japanese dishes like miso-marinated Black Cod.
The commercial fishery for Black Cod is well-established, with Alaska being the primary source of harvest. Sustainable fishing practices are in place to ensure the long-term viability of Black Cod populations.
While not a true member of the Cod family, Black Cod holds its own distinct place in the culinary world and is highly sought after for its unique taste and texture. Its dark, alluring appearance, coupled with its delicious flavor, has made it a prized delicacy enjoyed by seafood lovers around the world.
Habitat and Distribution
A. Natural Habitats where Cod Fish can be found:
Cod Fish are primarily found in cold-water habitats, particularly in the North Atlantic and North Pacific Oceans. They inhabit a variety of environments, including coastal areas, offshore waters, and deeper offshore regions. Here are some of the natural habitats where Cod Fish can be found:
1. Continental Shelf: Cod Fish are commonly found on the continental shelf, which is the gently sloping underwater extension of the continent. They are known to inhabit the upper and middle portions of the water column, often near the seafloor.
2. Coastal Areas: Cod Fish can be found in coastal regions, such as rocky shores, estuaries, and nearshore zones. They may seek shelter and forage among kelp beds, rocky reefs, and other coastal structures.
3. Submerged Structures: Cod Fish often gather around submerged structures, such as shipwrecks, artificial reefs, and underwater ridges. These structures provide shelter and attract prey, making them suitable habitats for Cod Fish.
4. Deep-sea Regions: Some species of Cod Fish, like the Greenland Cod, are adapted to survive in extreme cold conditions and can be found in deeper offshore areas. They may inhabit depths ranging from a few hundred feet to several thousand feet.
B. Distribution of Cod Fish across different regions:
Cod Fish have a wide distribution across different regions, mainly in the North Atlantic and North Pacific. Here’s a general overview of their distribution:
1. North Atlantic: The Atlantic Cod is primarily found in the cold waters of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is distributed along the coasts of North America, from Labrador and Newfoundland in Canada to the Gulf of Maine and as far south as Cape Hatteras in the United States. It is also present in European waters, including the North Sea, the Norwegian Sea, and the Barents Sea.
2. North Pacific: The Pacific Cod is prevalent in the northern Pacific Ocean. Its distribution extends from the Bering Sea and the Gulf of Alaska to the western coast of North America, including regions off Alaska, Russia, and Japan.
3. Arctic and Sub-Arctic Regions: The Greenland Cod, or Arctic Cod, is adapted to survive in extreme cold conditions and is found in the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. It is distributed around Greenland, Canada’s Arctic coast, and other areas within the Arctic Circle.
The distribution of Cod Fish is influenced by various factors, including water temperature, food availability, and suitable habitats. Understanding their natural habitats and distribution helps in better managing and conserving these important fish species in different regions.
Habits and Lifestyle
Cod Fish are fascinating creatures with distinctive habits and lifestyles that are shaped by their environment and biology. Here are some key aspects of their habits and lifestyle:
1. Feeding Habits: Cod Fish are opportunistic predators, meaning they are adaptable in their feeding habits. They primarily feed on a variety of prey, including smaller fish, crustaceans, squid, and other marine invertebrates. Their diet may vary depending on the availability of food in their habitat.
2. Nocturnal Behavior: Cod Fish exhibit nocturnal feeding behavior, which means they are more active and feed during the nighttime. This behavior allows them to avoid predators and efficiently hunt for prey in the cover of darkness.
3. Bottom-Dwelling: Cod Fish are primarily bottom-dwellers, meaning they spend a significant portion of their time close to the seafloor. They use their strong, muscular bodies and fins to navigate rocky or sandy bottoms, searching for food and shelter.
4. Migration: Some Cod Fish species undertake seasonal migrations. These migrations can be driven by changes in water temperature, food availability, and reproductive needs. During these migrations, Cod Fish may travel long distances to reach more favorable environments.
5. Social Behavior: Cod Fish can display schooling behavior, where they gather in groups for various reasons. Schooling provides them with protection against predators and allows them to cooperate in hunting for food.
6. Reproduction and Spawning: Cod Fish have complex reproductive behaviors. They typically spawn in specific areas during specific seasons, with the timing varying depending on the species and location. Females release large numbers of eggs into the water, and males release sperm to fertilize them externally.
7. Life Span: The life span of Cod Fish can vary among species and environmental conditions. Some species can live for several decades if they survive predation, fishing pressure, and other threats.
8. Adapting to Environmental Changes: Cod Fish have shown resilience and adaptability to changes in their environment. They can adjust their behavior, feeding patterns, and habitat preferences in response to fluctuations in water temperature, food availability, and other environmental factors.
Understanding the habits and lifestyle of Cod Fish is essential for their conservation and sustainable management. As with any species, their ecological roles and interactions within marine ecosystems play a crucial part in maintaining the balance and health of our oceans.
Diet
Cod Fish have a varied diet that includes a range of prey items. Here are some common food sources that make up the diet of Cod Fish:
Smaller Fish: Cod Fish feed on smaller fish species, such as herring, capelin, sand lance, and small codfish. These smaller fish provide a significant portion of their diet and serve as an important source of energy and nutrients.
Crustaceans: Cod Fish also consume crustaceans, including shrimp, crabs, lobsters, and small shellfish. These crustaceans are often found in the same habitats as Cod Fish and serve as a valuable food source.
Squid: Squid is another prey item that Cod Fish feed on. Squid are cephalopods with soft bodies and provide a nutritious food source for Cod Fish.
Marine Invertebrates: Cod Fish have been observed feeding on various marine invertebrates, such as worms, small mollusks, and crustaceans like amphipods and isopods.
The specific diet of Cod Fish can vary depending on their habitat, location, and the availability of prey. They are opportunistic predators, meaning they will adapt their feeding habits based on what is available in their environment. This flexibility allows them to thrive in different ecosystems and ensures they have access to sufficient food resources.
Health Benefits of Eating Cod Fish
Cod Fish is not only delicious but also offers numerous health benefits when included in a balanced diet. Here are some of the key health benefits of consuming Cod Fish:
1. Rich in Protein: Cod Fish is a great source of high-quality protein. Protein is essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues, including muscles, skin, and organs. Including Cod Fish in your diet helps meet your protein needs and supports overall body functions.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Cod Fish is known for its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These healthy fats are crucial for brain health, heart function, and reducing inflammation in the body. Regular consumption of Cod Fish can contribute to a healthy cardiovascular system and may help reduce the risk of heart disease.
3. Brain Health: The omega-3 fatty acids found in Cod Fish play a vital role in brain development and function. They are particularly beneficial for cognitive function, memory, and maintaining good mental health. Including Cod Fish in your diet, especially during pregnancy and early childhood, can support healthy brain development.
4. Nutrient-Rich: Cod Fish contains essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health. It is a good source of vitamin B12, which is necessary for nerve function and the production of red blood cells. Additionally, Cod Fish provides minerals like selenium, phosphorus, and iodine, which are important for various bodily functions.
5. Weight Management: Cod Fish is relatively low in calories and fat, making it a suitable choice for individuals who are conscious of their weight. It provides a lean source of protein that can help promote satiety, reduce hunger cravings, and support healthy weight management.
6. Heart Health: The omega-3 fatty acids in Cod Fish help maintain heart health by reducing the risk of heart disease. They can help lower blood pressure, reduce triglyceride levels, and improve overall cardiovascular function. Including Cod Fish in a heart-healthy diet, along with other nutritious foods, can have a positive impact on heart health.
7. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The omega-3 fatty acids in Cod Fish have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health conditions, including arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain cancers. Consuming Cod Fish may help alleviate inflammation and support overall well-being.
It’s important to note that while Cod Fish offers numerous health benefits, it’s essential to choose sustainably sourced fish and prepare it in a healthy way. Grilling, baking, or steaming Cod Fish is preferable to frying, as it retains more of its nutritional value. Including Cod Fish as part of a varied and balanced diet can contribute to a healthy lifestyle and overall well-being.
Techniques for Fishing Cod Fish:
Fishing for Cod Fish can be an exciting and rewarding activity. Different fishing techniques are employed to catch Cod Fish, depending on the location, fishing regulations, and personal preferences. Here are some common techniques used for fishing Cod Fish:
1. Bottom Fishing: Bottom fishing is one of the most popular techniques for catching Cod Fish. It involves dropping a baited hook or lure to the seafloor where Cod Fish typically reside. Anglers use specialized rigs, such as a cod rig or a fishfinder rig, with bait such as squid, herring, or clams to attract Cod Fish.
2. Jigging: Jigging is an active fishing technique that involves using a weighted lure, known as a jig, which is jerked or jigged up and down in the water column. This imitates the movement of injured or fleeing prey, attracting Cod Fish to strike. Jigging can be done from a boat or off a pier and requires skill and finesse to entice Cod Fish to bite.
3. Trolling: Trolling is a technique commonly used when fishing from a moving boat. It involves trailing a line with lures or bait behind the boat and slowly moving through the water. This technique can be effective for catching Cod Fish, especially when targeting larger individuals in open water or near underwater structures.
4. Drift Fishing: Drift fishing involves allowing the boat to drift naturally with the current while lines with bait or lures are cast out. This technique is effective when targeting Cod Fish in areas with strong currents or when covering a larger area in search of actively feeding fish.
5. Deep-Dropping: Deep-dropping is a specialized technique used to target Cod Fish in deeper waters. It involves using heavy sinkers and specialized rigs to reach the depths where Cod Fish are known to reside. This technique requires specialized equipment and knowledge of the fishing grounds.
6. Ice Fishing: In colder regions, ice fishing is a popular method for catching Cod Fish. Anglers drill holes in the ice and set up lines with bait or lures beneath the ice. Ice fishing for Cod Fish requires proper safety precautions and knowledge of ice conditions.
It’s important to note that fishing regulations and seasons may vary depending on the location and specific Cod Fish species. It’s crucial to adhere to local fishing regulations, size limits, and bag limits to ensure sustainable fishing practices and the conservation of Cod Fish populations.
Cod Fish Farming:
Cod fish farming, also known as cod aquaculture or cod mariculture, is the practice of rearing cod fish in controlled environments such as fish farms or aquaculture facilities. This method of farming provides an alternative to traditional wild-caught fishing and helps meet the demand for cod fish while reducing pressure on wild populations. Here are some key points about cod fish farming:
1. Controlled Environment: Cod fish farming involves creating an environment that mimics the natural habitat of cod fish, providing optimal conditions for their growth and development. This typically involves large tanks or ponds with regulated water temperature, quality, and feeding regimes.
2. Hatcheries and Fingerlings: Cod fish farming often begins with the production of cod fish fingerlings (young fish) in hatcheries. Eggs are collected from mature cod fish, fertilized, and hatched in controlled conditions. The fingerlings are then reared in tanks until they reach a suitable size for transfer to grow-out facilities.
3. Grow-out Facilities: Cod fish are reared in larger tanks, cages, or net pens in grow-out facilities. These facilities are designed to provide ample space for the fish to grow and swim while ensuring proper water quality and feeding. Feed formulations are carefully selected to meet the nutritional needs of the fish and promote healthy growth.
4. Feed and Nutrition: In cod fish farming, specially formulated feed is provided to the fish to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth. The feed usually consists of a balanced mix of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Some cod fish farms also incorporate sustainable and environmentally friendly feed ingredients to minimize the ecological footprint.
5. Disease Management: Disease prevention and management are critical in cod fish farming. Farms implement strict biosecurity measures to reduce the risk of disease outbreaks. Regular health monitoring, vaccination programs, and proper water management practices help maintain the health and well-being of the fish.
6. Environmental Considerations: Sustainable cod fish farming practices prioritize minimizing environmental impacts. Farms employ technologies to monitor and manage water quality, optimize feed usage, and reduce waste production. Efforts are made to prevent escapes and minimize interactions with wild populations.
Cod fish farming has the potential to provide a consistent supply of cod fish, reduce pressure on wild populations, and support local economies. However, it is important to ensure that cod fish farming operations adhere to strict environmental and ethical standards to promote sustainability and minimize potential negative impacts on the environment and wild fish populations.
As with any form of aquaculture, cod fish farming should be carried out in a responsible and sustainable manner, with a focus on minimizing the ecological footprint, ensuring fish welfare, and maintaining the long-term health and viability of both the farmed fish and the surrounding ecosystems.
Mating Habits and Reproduction of Cod Fish:
Cod Fish have unique mating habits and reproductive strategies that contribute to their population growth. Here are some key points about the mating habits and reproduction of Cod Fish:
1. Spawning Season: Cod Fish typically have a specific spawning season when they gather in large numbers to reproduce. The exact timing of the spawning season varies depending on the species and geographical location. Generally, spawning occurs during the spring or early summer when water temperatures are favorable.
2. Spawning Behavior: Cod Fish are broadcast spawners, which means that the female releases a large number of eggs into the water, and the male fertilizes them externally. Spawning usually takes place in shallow coastal areas or over rocky reefs, where the eggs have a higher chance of survival.
3. Egg Production: A mature female Cod Fish can produce hundreds of thousands to millions of eggs during a single spawning event. The number of eggs produced depends on the size and age of the fish. The eggs are small and buoyant, allowing them to float in the water column.
4. Egg Development: After fertilization, the eggs undergo a period of development. The duration of egg development varies depending on water temperature and other environmental factors. It can take several days to weeks for the eggs to hatch into larvae.
5. Larval Stage: Once the eggs hatch, the larvae emerge. They are initially very small and have limited swimming abilities. Larval Cod Fish drift in the ocean currents, feeding on microscopic plankton for nourishment. This stage is crucial for their survival and growth.
6. Juvenile Stage: As the larvae grow, they undergo various physical and behavioral changes. They develop into juvenile Cod Fish and gradually transition to a benthic (bottom-dwelling) lifestyle. During this stage, they start feeding on small prey items and continue to grow and develop.
7. Maturation and Reproductive Cycle: Cod Fish reach sexual maturity at different ages, depending on the species and environmental conditions. It can take several years for Cod Fish to reach reproductive maturity. Once mature, they participate in the spawning process and continue the reproductive cycle to ensure the survival and growth of future generations.
Conservation Status of Cod Fish:
The conservation status of Cod Fish varies depending on the specific species and the region in which they are found. Here is an overview of the conservation status of some commonly known Cod Fish species:
Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua): The Atlantic Cod, once abundant in the North Atlantic Ocean, has experienced significant declines in population due to overfishing and habitat degradation. As a result, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists the Atlantic Cod as vulnerable to extinction.
Pacific Cod (Gadus macrocephalus): The Pacific Cod is more abundant than its Atlantic counterpart. It is not currently listed as a threatened species by the IUCN. However, sustainable fishing practices and proper management are still necessary to prevent population declines.
Greenland Cod (Gadus ogac): The Greenland Cod, also known as Arctic Cod, is found in the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. While specific population assessments may vary, this species is generally considered stable, and its conservation status is not of immediate concern.
Taking Care of Cod Fish as Pets:
If you’re considering keeping Cod Fish as pets, it’s important to provide them with a suitable environment and proper care to ensure their health and well-being. Here are some key points to consider when taking care of Cod Fish:

1. Aquarium Setup: Cod Fish require a spacious aquarium with ample swimming space. The tank should be large enough to accommodate their size and should ideally have a capacity of at least 50 gallons per fish. It’s important to maintain appropriate water parameters, including temperature, pH level, and salinity, that mimic their natural habitat.

2. Water Quality: Cod Fish are sensitive to water quality, so it’s crucial to regularly test the water parameters and maintain proper filtration. Use a reliable filtration system to keep the water clean and remove any waste or debris. Regular water changes are also necessary to maintain optimal water quality.

3. Temperature and Lighting: Cod Fish thrive in cool water temperatures ranging from 40°F to 60°F (4°C to 15°C). It’s essential to provide a suitable cooling system or adjust the room temperature accordingly. Additionally, ensure the aquarium is properly lit with appropriate lighting to simulate natural day and night cycles.
4. Diet and Feeding: Cod Fish are carnivorous and require a diet rich in protein. Feed them high-quality commercial fish pellets or flakes specifically formulated for marine fish. Additionally, supplement their diet with frozen or live foods such as brine shrimp, krill, and small fish to provide a varied and balanced diet.
5. Tankmates and Compatibility: When selecting tankmates for Cod Fish, consider their compatibility with other species. Avoid keeping them with aggressive or territorial fish that may harm or stress them. It’s best to keep Cod Fish in a species-specific tank or with other peaceful, cold-water fish that share similar water requirements.
6. Environmental Enrichment: Provide a suitable environment for your Cod Fish by adding appropriate decorations, such as rocks, caves, and plants, to mimic their natural habitat. This creates hiding spots and adds visual interest to the aquarium. Ensure the decorations are safe and do not have sharp edges that could injure the fish.
7. Monitoring and Observation: Regularly observe your Cod Fish for any signs of illness or stress. Look out for abnormal behavior, loss of appetite, or physical abnormalities. If you notice any issues, consult a qualified aquatic veterinarian or seek advice from a knowledgeable fish expert to address the problem promptly.
Remember that Cod Fish are primarily wild-caught species and require specific care to thrive in captivity. They may not be suitable for beginner aquarists due to their specialized needs. It’s crucial to research and understand their requirements thoroughly before deciding to keep them as pets.
Lastly, it’s important to ensure the legality of owning Cod Fish as pets in your area. Check local regulations and consult with fishkeeping authorities to ensure compliance with any licensing or permitting requirements.
Common Diseases of Cod Fish and Their Treatments:
Cod Fish, like any other fish, can be susceptible to various diseases. It’s important to monitor their health and take prompt action if any signs of illness are observed. Here are some common diseases that can affect Cod Fish and their potential treatments:
1. Ich (Ichthyophthirius multifiliis):

– Symptoms: White spots resembling grains of salt on the fish’s body and fins, scratching against objects.
– Treatment: Increase water temperature gradually to around 82-86°F (28-30°C) to accelerate the lifecycle of the parasite. Treat the tank with an appropriate ich medication containing active ingredients like malachite green or copper.
2. Fin Rot:

– Symptoms: Frayed, eroded, or disintegrating fins, redness, inflammation, or whitish film on the affected areas.
– Treatment: Maintain pristine water quality and remove any decaying matter from the tank. Administer antibacterial medications, such as antibiotics or fin rot treatments, following the instructions provided.
3. Velvet Disease (Oodinium):

– Symptoms: A fine, golden or rust-colored dust-like appearance on the fish’s body, clamped fins, scratching against objects.
– Treatment: Increase water temperature gradually to around 82-86°F (28-30°C). Administer medications specifically formulated to treat velvet disease, such as copper-based medications or malachite green.

– Symptoms: Open sores, ulcers, redness, swelling, or discoloration of the skin, lethargy, loss of appetite.
– Treatment: Isolate the affected fish to prevent the spread of infection. Administer broad-spectrum antibiotics or antibacterial treatments suitable for treating bacterial infections in fish. Follow the instructions provided by the medication manufacturer.

– Symptoms: Visible worms in the fish’s feces, weight loss, lethargy, decreased appetite.
– Treatment: Administer an appropriate antiparasitic medication specifically designed to target internal worms in fish. Ensure proper dosage and treatment duration according to the instructions provided.

– Symptoms: Cotton-like growths on the fish’s body, fins, or gills, discoloration, redness, or fraying of the affected areas.
– Treatment: Isolate the affected fish to prevent the spread of the fungus. Administer antifungal medications or treatments containing active ingredients like malachite green or methylene blue.
If you suspect that your Cod Fish is unwell or showing signs of disease, it is recommended to consult with a qualified aquatic veterinarian or seek advice from experienced fishkeepers. They can provide accurate diagnoses and recommend suitable treatments for specific diseases.
Prevention is key in maintaining the health of Cod Fish. Ensure proper tank hygiene, regular water quality testing, balanced nutrition, and a stress-free environment to minimize the risk of diseases. Quarantine new fish before introducing them to the main tank to prevent potential disease transmission.
Always follow the instructions provided by medication manufacturers, and remember to carefully read and understand the potential side effects and precautions associated with the treatments.
Fun and Fascinating Facts about Cod Fish:
1. Longevity: Cod Fish have an impressive lifespan, with some individuals living up to 25 years or even more in the wild.
2. Size Matters: Cod Fish can grow to be quite large. The largest recorded Atlantic Cod weighed around 211 pounds (95.7 kg) and measured over 6 feet (1.8 meters) in length.
3. Cold-Water Champions: Cod Fish are well-adapted to cold waters and can survive in temperatures as low as 32°F (0°C). Their ability to thrive in chilly environments makes them an iconic species of the North Atlantic and Arctic regions.
4. Changing Colors: Cod Fish have the ability to change their coloration based on their surroundings. They can be lighter in color when swimming in shallow waters or near the surface and darker when in deeper waters or near the seabed.
5. Mouth Full of Teeth: Cod Fish have a mouthful of sharp teeth, which they use to capture and consume their prey. Their teeth are well-suited for their carnivorous diet.
6. Exceptional Swimmers: Cod Fish are fast swimmers and can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour (40 kilometers per hour) when they need to.
7. Vital Fisheries: Cod Fish have been a vital part of commercial fisheries for centuries, with their meat being highly sought after for its taste and texture. They have played a significant role in the fishing industry and the economies of many coastal communities.
8. Air Bladders: Cod Fish have a unique feature called an air bladder, which helps them control their buoyancy in the water. By inflating or deflating the air bladder, they can adjust their position in the water column.
9. Spawning Spectacle: During the spawning season, Cod Fish gather in large groups, creating impressive spawning aggregations. These gatherings are essential for successful reproduction and contribute to the species’ population dynamics.
10. Historical Significance: Cod Fish have a rich cultural and historical significance. They have been an important food source for various indigenous communities and have played a significant role in the exploration and colonization of North America.
11. Symbolic Representation: Cod Fish have become symbols of resilience and adaptability. Their ability to withstand changing environmental conditions and rebound from population declines has made them a symbol of hope for conservation efforts.
These fascinating facts about Cod Fish highlight their unique characteristics and their ecological and cultural importance. Whether it’s their size, adaptability, or historical significance, Cod Fish continue to captivate the interest of people around the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cod Fish are remarkable creatures that inhabit the cold waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, the northern Pacific Ocean, and the Arctic regions. With their scientific name Gadus morhua, they are one of the most iconic and commercially important species in the world. From their impressive size and longevity to their unique adaptations and behaviors, Cod Fish have captivated the attention of fish enthusiasts, scientists, and fishermen alike.
Cod Fish come in various species, including the Atlantic Cod, Pacific Cod, Greenland Cod, and others. While the Atlantic Cod remains the most well-known and sought-after species, the Pacific Cod and Greenland Cod also hold their own significance. Additionally, the term “Rock Cod” is used to refer to several species that resemble true cod in appearance.
These fish possess a distinct appearance, with their elongated bodies, prominent jaws, and sharp teeth. They are well-adapted to cold water environments and display fascinating behaviors in their natural habitats. Cod Fish are carnivorous predators with a diverse diet, feeding on small fish, crustaceans, and other marine organisms.
Apart from their ecological importance, Cod Fish have also played a significant role in human history and culture. They have been a staple food source for coastal communities, contributing to local economies and culinary traditions. Furthermore, Cod Fish exhibit various health benefits, being a good source of lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential nutrients.
However, it is crucial to consider the conservation status of Cod Fish. Overfishing, habitat degradation, and climate change pose significant threats to their populations. Conservation efforts and sustainable fishing practices are necessary to ensure the long-term survival of these iconic species.
Whether you are fascinated by their biology, intrigued by their historical significance, or enjoy their culinary delights, Cod Fish continue to capture the imagination of people worldwide. Their unique traits, adaptations, and cultural importance make them a subject of study, admiration, and conservation.
In conclusion, Cod Fish are not only a symbol of our interconnectedness with the oceans but also a reminder of our responsibility to protect and preserve the diverse marine life that enriches our planet. By understanding and appreciating these incredible creatures, we can work towards their conservation and ensure a sustainable future for Cod Fish and the marine ecosystems they inhabit.
Cod Fish FAQs
How long do Cod Fish typically live?
Cod Fish have an average lifespan of 15 to 25 years, although some individuals can live longer.
How fast can Cod Fish swim?
Cod Fish can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour (40 kilometers per hour) when necessary
What is the average weight of a Cod Fish?
Cod Fish can vary in weight depending on the species and environmental factors. On average, adult Cod Fish can weigh between 11 and 33 pounds (5 to 15 kilograms).
What is the average length of a Cod Fish?
Cod Fish can grow to an average length of 2 to 4 feet (60 to 120 centimeters), with some individuals reaching even larger sizes.
Are Cod Fish dangerous or do they pose a threat to humans?
Cod Fish are not considered dangerous to humans. They are generally docile and not known to attack or pose a threat to humans. However, as with any wild animal, it is important to exercise caution and respect their space when encountering them.
Can Cod Fish be eaten?
Yes, Cod Fish are widely consumed around the world and are considered a popular food fish. They are known for their white, flaky flesh and mild flavor./p>
Are there any health benefits to eating Cod Fish?
Yes, Cod Fish is a nutritious food choice. It is a good source of lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Consuming Cod Fish can contribute to a healthy diet and provide various health benefits, including heart health and brain function.
What are the main fishing techniques used to catch Cod Fish?
Common fishing techniques for catching Cod Fish include bottom trawling, longlining, jigging, and using baited hooks. The specific method used may vary depending on the fishing location and regulations in place.
What is the conservation status of Cod Fish?
The conservation status of Cod Fish varies depending on the specific species and region. Some Cod Fish populations, such as the Atlantic Cod, have faced significant declines due to overfishing and habitat degradation. Conservation efforts and sustainable fishing practices are important to protect and restore Cod Fish populations and their ecosystems.